 Full
FullGuide »
THIS SECTION CONSISTS OF GENERAL COMMENTS ON WEED CONTROL IN PEAS FOLLOWED BY DETAILS OF PRODUCTS/ACTIVE INGREDIENTS, WEED CONTROL CHECKLISTS AND A PHOTO SECTION WITH REFERENCE IMAGES OF WEEDS.
Good weed control is essential in the pea crop, since it is not very competitive and is easily dominated by weeds. Efficient control will ease combining and facilitate rapid drying in addition to increasing yield. A number of pre- and post-emergence herbicides are available. These notes, partly based on the results of PGRO experimental work, are intended to help growers choose wisely.
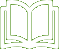
General control of annual broad- leaved weeds can be achieved pre-emergence with a soil-applied residual herbicide or, when weeds and crop have both emerged, with a foliar- applied post-emergence herbicide.
Where soil type allows, it is advisable to use a pre-emergence herbicide. It removes weed competition early and gives better control of some weeds, for example, knotgrass and annual meadow-grass. However, adequate soil moisture is needed for good efficacy of a residual herbicide.
Post-emergence sprays can be applied from 3 nodes of the crop to well-waxed peas (tested with crystal violet dye).
Volunteer oilseed rape can be a serious problem if it is grown in the same rotation and control, particularly of rape germinating from depth, may be incomplete.
Infestations of wild-oats can cause severe yield reduction and interfere with harvesting. They must be controlled to avoid re-seeding in the following crop.
Couch is best controlled with products containing glyphosate pre-harvest of cereals, or in the autumn, or pre-harvest of peas (except for seed crops). Although some graminicides offer control, recommended application rates are uneconomically high.
Post-emergence graminicides can control volunteer cereals and offer some reduction of black-grass and other grass weeds, however, resistant grass weed populations will cause problems. Control with graminicides, particularly of high populations of black-grass can be disappointing. Where black-grass is anticipated to be a problem, it is recommended that populations are depleted as much as possible by ploughing and the use of stale seedbeds prior to drilling.
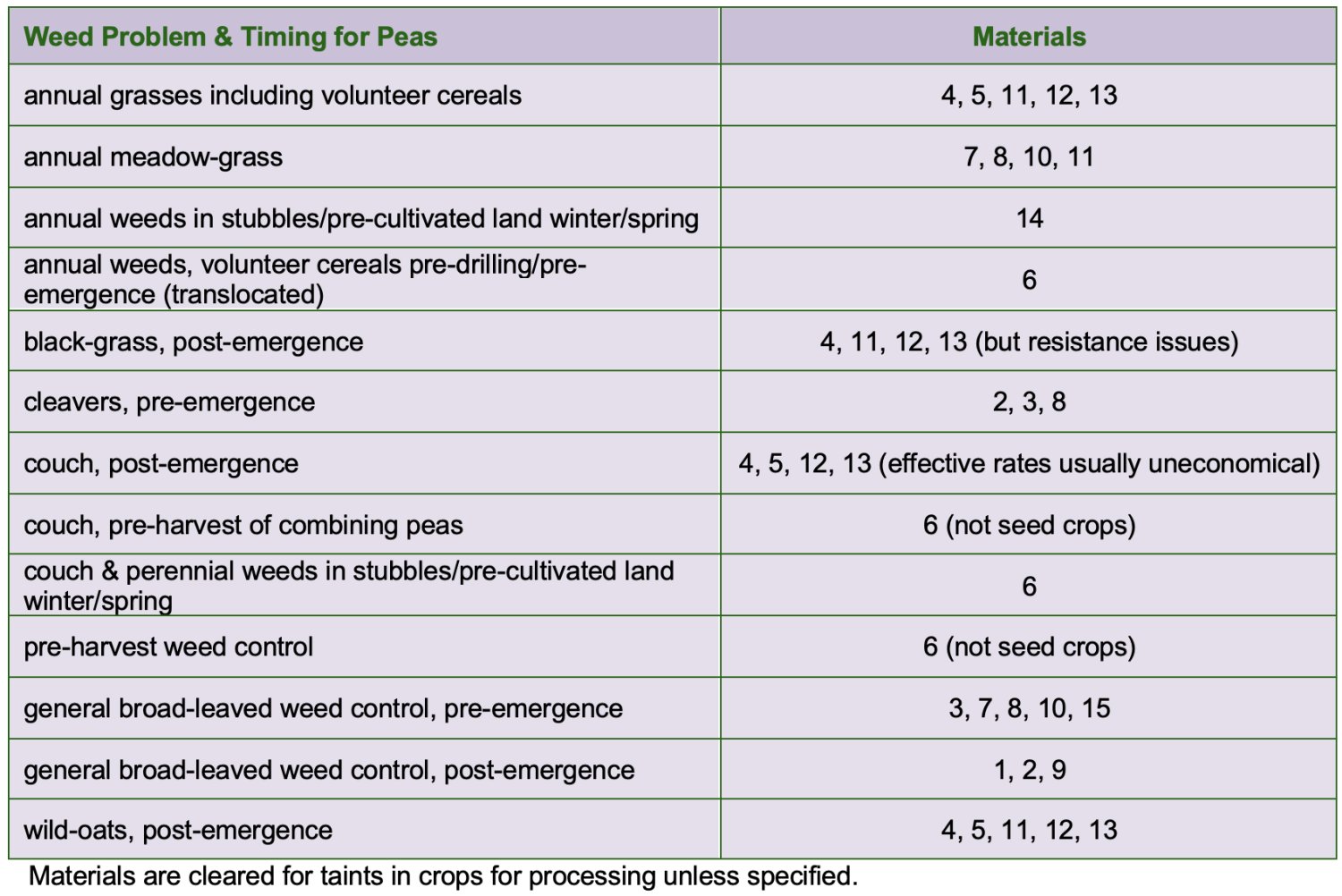
At the end of this section there is a checklist of active ingredients and approved products for combining peas, a checklist of weed problem & timing for combining peas and a checklist of weed susceptibility to herbicides for combining peas.
There is also a set of reference images of weeds relevant to combining peas.
Several products are available for controlling weeds in peas and it is important that growers appreciate the properties of each and that they choose the one most suitable for their conditions, soil type and weed spectrum. These notes, based on the results of PGRO experimental work, are intended to help growers choose wisely.
For most pre-emergence pea herbicides there are recommendations that the land is ploughed or deep cultivated before sowing the following crop - please check the label.
Where buffer zones are required near surface waters or ditches these are denoted by BZ Category A or B. A LERAP can be applied to category B OR more recently specific product instruction regarding the required BZ.
Experiments have shown benefits of early weed removal and it is best to use pre-emergence materials where possible. Pre-emergence residual herbicides require soil moisture for activity and are suitable for all except late drillings where conditions are often drier. Pre-emergence herbicides are ineffective at economic rates on highly organic soils, and some are damaging on gravelly or very light soil types. They are less effective on cloddy seedbeds and rolling the seedbed to provide a level surface is essential for good weed control with pre-emergence materials.
These are not controlled by pre-emergence applications and the effects of post-emergence sprays vary. Mixtures containing MCPB will give useful control of volunteer oilseed rape, thistles and docks, or the material may be used alone. Perennial weeds may also be eradicated with glyphosate pre-harvest of the preceding wheat or barley crop.
Pendimethalin (various products) LERAP: B
Pendimethalin should be applied as soon as possible after sowing. It may be used on any variety on all except organic or gravelly soils. Pendimethalin should not be used on soils where surface water is likely to accumulate. Maximum permissible rates of pendimethalin products controls volunteer rape, AMG, speedwells, knotgrass and chickweed amongst others but, control of mayweed is variable, and charlock and mustard are resistant. The activity of pendimethalin is very moisture dependent.
Be aware that there are various pendimethalin products which have different approved rates of use in dry peas because they differ in the concentration of pendimethalin present e.g. there are 400, 455 and 330 gai/l formulations.
Clomazone (various products) LERAP: n/a
A pre-emergence residual herbicide for the control of cleavers and other broad-leaved weeds. As well as cleavers it has good activity on chickweed, shepherd’s purse, fools parsley and red dead-nettle, but control of other species can be variable. As it’s spectrum of activity is quite narrow it is usually tank mixed with other pre-emergence products.
Nirvana (pendimethalin+imazamox) LERAP: B
Nirvana is used pre-emergence and provides wide spectrum residual broad-leaved weed control.
Nirvana is crop safe on all commercially available varieties. Seed should be drilled to a depth of 25 mm and fields prone to water logging should be avoided.
Maximum persistence is seen with the full permitted dose of 4.5 l/ha and this may allow a ‘one-hit’ herbicide programme. The 3.0 l/ha application appears to be a good compromise with possibly the additional option of a further drop to 2.5 l/ha when considering a mix with clomazone to maximise cleaver control. Work has shown the full 4.5 l/ha application reduced cleaver numbers effectively and may be a means of retaining the full weed control spectrum while still achieving adequate cleaver control. It shows excellent activity against polygonums, black-bindweed, redshank and knotgrass. Charlock is also effectively controlled as is chickweed. Nirvana also gives improved control of early emerging volunteer oilseed rape when compared to pendimethalin alone.
Stallion Sync TEC (pendimethalin + clomazone): LERAP Aquatic buffer zone 5m.
A micro encapsulated broad-spectrum pre-emergence product with useful cleaver activity. Other weeds which are effectively controlled include shepherd’s purse, fat hen, deadnettle’s, annual mercury, knotgrass, groundsel, black nightshade speedwells and field pansy amongst others.
Emerger (Aclonifen)
Aclonifen gained approval in 2023.
It may sometimes be necessary to apply a follow-up post-emergence herbicide if pre-emergence treatments have not given adequate control. Those treatments which a have a ‘contact’ action (bentazone treatments) must be applied to healthy peas which are well waxed. Pea leaf wax can be tested with crystal violet solution. There is a PGRO information sheet on Pea leaf wax assessment.
MCPB (Tropotox) LERAP: N/A
This material is specifically used to control thistles and docks and will effectively stunt volunteer oilseed rape. It only controls a limited range of annual weeds and so a bentazone + MCPB mix will be required to enhance the controlled weed spectrum. Apply before peas are at enclosed bud stage.
MCPB + bentazone tank-mix. LERAP: N/A
This tank-mix is relatively expensive the margin of crop safety is less compared to using the products individually. However, this mixture is capable of giving good weed control including cleavers and large volunteer oilseed rape under a wide range of conditions. Crops under stress may be checked. Peas should not be sprayed under conditions of high temperatures or humidity. Apply a single application from 3 node to before flower bud can be found in terminal shoot.
Bentazone (Basagran SG, Benta 480, Clayton Baritone). LERAP: N/A
Please note, there have been changes to the Basagran SG label and rates of application and number of applications permitted in peas altered. There is also advisory information regarding water stewardship with the aim of maximising product longevity. For the moment other bentazone product labels are as they were but please check. Bentazone can be used alone and is useful for cleaver control but is ineffective on large fat-hen and some other weeds including knotgrass and speedwells. Please check labels for specific product for earliest application timings, usually from 2 to 3 nodes, latest applications before flower buds detectable in terminal shoots.
Oilseed rape: This can be a problem weed several years after cropping. Allowing shed seed to germinate after harvest, before ploughing or cultivating, will help prevent carry over.
Products containing pendimethalin are the only pre-emergence herbicides which can control rape volunteers, but control may be incomplete and those germinating from depth will not be killed.
A cheap post-emergence application of MCPB will effectively control smaller specimens. Bentazone post-emergence is effective. Do not expect control of rape beyond 4 true leaf stage. Bentazone + MCPB may be needed where rape volunteers are at an advanced stage. If rape is not controlled in a combining pea crop an application of an appropriate glyphosate product pre-harvest may be required. Approved glyphosate products are slow to act.
Potatoes: Competition from volunteer potatoes can be severe, but it is not possible to selectively kill potatoes in combining pea crops.
The selective post-emergence grass weed killers, fluazifop-p-butyl, quizalofop-p-ethyl and cycloxydim will not control annual meadow-grass. Propaquizafop gives some suppression but only if applied up to 3 leaf stage. Pre-emergence residual herbicides containing pendimethalin offer some control annual meadow-grass.
Where graminicides are used in sequence with other post-emergence treatments, care must be taken that the crop has recovered and is undamaged (see labels).
Falcon and others (propaquizafop)
Falcon is a post-emergence treatment for wild-oats, optimum timing from two leaves folded to early tillering. Falcon may be applied to peas at 3rd node stage until when flower buds are visible. Minimum harvest interval is 7 weeks. No adjuvant is needed, and it is rain-fast after one hour following application.
Laser and others (cycloxydim)
Laser + Toil adjuvant oil (at 0.5% final spray volume) is a post-emergence treatment for control of wild-oats and other grasses. Optimum timing is at two fully expanded leaves to the end of tillering. The peas should be from 3rd node stage until before crop canopy prevents adequate spray penetration. Test pea leaf wax before application. Minimum harvest interval is 5 weeks.
Fusilade Max and others (fluazifop-p-butyl)
Fusilade Max requires no additional wetters. Applications should be made to peas from 4 node stage before first flower visible, and pea leaf wax should be tested. The wild oats should be from 2 leaf to fully tillered stages. Minimum harvest interval is 2 weeks. Check product labels for dose rates.
Leopard 5 EC (quizalofop-p-ethyl)
Timing for wild oats is from two leaves to fully tillered growth stage. It may be applied to peas before the crop canopy closes. Minimum Harvest Interval for vining and combining peas is 5 weeks.
Panarex (quizalafop-p-tefuryl)
Is a post-emergence graminicide for the control of wild-oats and other grasses. Spring applications only are permitted but can be made from 2-3 unfolded leaves up to flower buds visible. It has a 60 day harvest interval.
Pre-emergence herbicides for broad-leaved weeds will have little effect on germinating black-grass, but where extensive late germination is expected the most satisfactory control will be obtained by integrating cultural techniques and chemical options e.g., Fusilade Max (and others), Leopard 5 EC, Falcon, Panarex or Laser. A different approach will be needed where resistant black grass occurs and specialist advice should be sought.
Volunteer cereals can be controlled by the wild-oat rate of the post-emergence herbicides, Fusilade Max (and others), Panarex and Falcon, and at a slightly higher rate than that for wild-oats for Laser.
The best and most economical means of control is by application of one of the various glyphosate products either pre-harvest in the previous cereal crop or in the autumn. Some control of this weed can be achieved by standard autumn cultivations or graminicide treatments.
Laser controls couch and can be used at 2.25 l/ha + Toil as a selective post-emergence treatment in peas, when couch is 15 cm tall (4 - 9 expanded leaves up to end of tillering). Leopard 5 EC from 4 leaves to before jointing.
No other post-emergence graminicides are approved for peas at rates for control of perennial grasses. Fusilade Max (no adjuvant required) applied at wild-oat rates gives useful suppression of couch foliage. These post-emergence graminicides will not give long-term couch control and at the higher rates suggested are usually uneconomic.
There are recommendations for control of barren brome using, Laser or Fusilade Max (and others) post-emergence.